Restoring Health to Your Teeth & Gums
Endodontics & Periodontics
At Chemung Family Dental, we are committed to keep your teeth, gums, and smile healthy. We offer comprehensive endodontic and periodontal services to restore health to your mouth and to prevent future issues from developing. We work with each patient to design personalized treatment plans so they see tailored, effective results and improvements to their health.
Endodontics
Your natural teeth are meant to last a lifetime! If one of your teeth should become critically injured or diseased, it can oftentimes be saved through a specialized dental procedure known as endodontic treatment. To help you understand when and why such a procedure might be needed and how a damaged tooth can be saved, we have answered some of the most frequently asked questions about endodontic treatment.
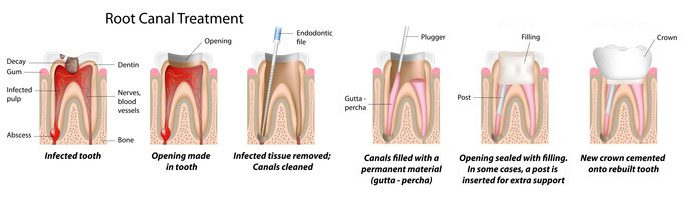
What are the steps of a root canal?
1. An abscessed (infected) tooth caused by tooth decay.
2. An opening is made through the crown of the tooth into the pulp chamber.
3. The pulp is removed, and the root canals are cleaned, enlarged and shaped.
4. The root canals are filled.
5. A metal post may be placed in the root canal for structural support.
6. The crown of the tooth is restored.
What should I do to prevent infections & root canals?
In order to maintain healthy teeth and prevent future dental disease, you should:
- Brush twice daily with a fluoride toothpaste that bears the ADA Seal of Acceptance
- Clean between your tooth once dally using floss or other interdental cleaners
- Eat balanced meals and limit the number of between-meal snacks
- Visit your dentist regularly
- Use ADA-accepted oral hygiene products.
These measures will help you keep your natural teeth and enjoy good dental health for a lifetime.
Endodontic/Root Canal FAQs
What is Endodontics?
Endodontics is the area of dentistry concerned with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of disorders of the dental pulp (the tooth’s soft core) Years ago teeth with diseased or injured pulps were extracted. Today, endodontic treatment gives dentists a safe and effective means of saving teeth.Anyone needing dentures should give serious consideration to Implants for the freedom they provide. Dr. Dunn and the staff at Chemung Family Dental have been informative, supportive and caring throughout my many implant procedures. And though I now live over 25 miles away, I continue to get my dental care at their office because I greatly appreciate that Dr. Dunn takes time to answer all my questions, is always professional and stays abreast of leading edge dental technology.
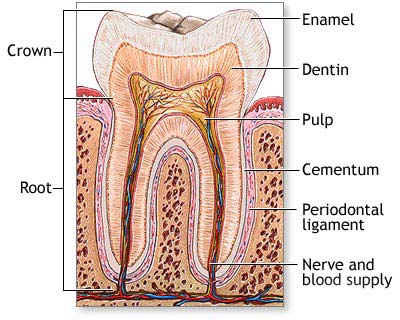
What is dental pulp?
The pulp is a soft tissue that contains the nerves, arteries, veins and lymph vessels of a tooth. It lies within the dentin, the bone-like tissue that supports the enamel. Within the dentin, the pulp extends from the pulp chamber in the crown (the portion of the tooth visible above the gums) down to the tip of the root by way of the root canal. All teeth have only one pulp chamber, but teeth with more than one root will have more than one canal.
What happens to the damaged pulp?
Why does the pulp need to be removed?
What does endodontic treatment involve?
Treatment usually requires from one to three appointments. During these treatments, your dentist or a specialist called an endodontist removes the diseased pulp. The pulp chamber and root canal(s) of the tooth are then cleaned, shaped and sealed to prevent recontamination of the root canal therapy usually is a relatively painless procedure.
What material will be used for the crown?
Why couldn't you just remove the tooth?
As a result, other teeth may be lost if the missing tooth is not replaced.A replacement tooth (an implant or a bridge) is usually more expensive than endodontic treatment and involves more extensive dental procedures on adjacent teeth. Endodontic treatment can safely and comfortably save a tooth that otherwise would have to be removed. In fact root canal therapy is successful approximately 95% of the time. Remember, a healthy restored tooth is always better than an artificial one.
How long will the restored tooth last?
Periodontics
At some point most people will suffer from periodontal disease. Periodontal disease affects the gums and bone supporting the teeth. You may have it and not even know it. There are no early warning signs, except for occasional bleeding and redness around the gums when brushing, and mouth odor.
However, as the disease progresses, the symptoms become more obvious. If left untreated, periodontal disease can lead to loosening of teeth, receding gums, and gum discomfort.
What are the stages of gum disease?
Stage 1. Gingivitis
In this early stage, your gums may look normal but they also may be red, puffy, and bleed easily when you brush your teeth. You also may notice some mouth odor. This is because bacteria in plaque have caused infection.
Stage 2. Early Periodontitis
Early periodontitis occurs when the bacterial infection spreads from the gum to the bone that support the teeth. The bacteria then cause small spaces, or crevices, to form between the gums. These crevices are called pockets. They are deeper than normal spaces, which measure 1 to 3 mm deep. Bacteria in the pocket also can destroy some bone.
As the pocket grows and the amount of bacteria increases, the gums recede down the root of the tooth, increasing the pocket depth. Your dentist measures how deep your pocket is with an instrument called a peridontal probe, which is placed in the gum crevice.
Stage 3. Moderate Periodontitis
When the gum has crept further down the root, it is called moderate periodontitis. In this stage, up to one-third on your bone has been lost.
Stage 4. Advanced Periodontitis
When half or more of the original bone holding the tooth has been lost, and pockets are very deep, it is called advanced periodontitis. The tooth may appear longer because the root is exposed, and the tooth may loosen and eventually fall out, or have to be removed by your dentist.
Periodontic FAQs
Don’t Wait Until It Hurts!
Periodontal disease is painless. It affects 75% of the population and often victims are unaware. It may also affect your overall health. There are warning signs that the American Dental Association and our staff want you to be aware of.
- Do your gums bleed when you brush your teeth or tooth pick between them?
- Are your gums red, swollen, or tender?
- Are your gums pulling away from your teeth?
- Do you see pus between your teeth and your gums when the gums are pressed?
- Are your permanent teeth loose and separating?
- Is there any change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite?
- Is there any change in the fit of your partial dentures?
- Do you have persistent bad breath?
If the answer is yes to any of these questions, bring it to the attention of your dentist or hygienist.
What causes periodontal disease?
Plaque that is not removed by regular brushing and flossing hardens into tartar over time. You cannot remove tartar (or calculus) on your own. The only way to remove tartar is by a procedure called scaling, which is done by a dentist.
What do you treat and prevent Periodontitis?
If you do have periodontal disease, your dentist or dental hygienist will remove the calculus above and below the gum. This procedure is called scaling. In moderate or severe periodontitis, it may be necessary to smooth the root surfaces of the teeth.
This procedure, called root planing, removes residual calculus and bacterial by-products. Your dentist may also replace old crowns and fillings that no longer fit well because these trap bacterial and food that can cause severe periodontal problems.
Is gum disease linked to heart attacks?
People with periodontal disease (over one half the adult population) have an infection that causes chronic inflammation of the gums. Also, it is a path for these bacteria to enter the bloodstream.
A recent study describes the association between heart disease and gum disease to be at least as strong as the linkage of heart disease to cholesterol, body weight, or smoking.
Why does the pulp need to be removed?
Should you have any questions or require additional information, please feel free to call us at 607-734-2045 or click to contact us directly.










Chemung Family Dental
1007 Broadway St.
Elmira, NY 14904
Tuesday 7:00 AM - 4:00 PM
Wednesday 7:00 AM - 4:00 PM
Thursday 7:00 AM - 2:00 PM
Friday Closed
Saturday Closed
Sunday Closed
